#Library
library("mgrtibbles")
#Data
amphibian_div_tbl <-
mgrtibbles::amphibian_div_tbl |>
#Select to retain only the iucn_2cat and Order columns
dplyr::select(iucn_2cat,Order,Family) |>
#Drop any rows with an NA
tidyr::drop_na()Geom bar

Bar charts are commonly used to display the counts of different categorical values.
In this page we will create bar charts with ggplot2::geom_bar(). Through examples we will demonstrate creating:
- The default bar chart
- A flipped bar chart
- A stacked bar chart using a second categorical variable
- A side-by-side bar chart using a second categorical variable
- A relative proportion bar chart
Dataset
For demonstration we’ll load the amphibian_div_tbl data from the mgrtibbles package (hyperlink includes install instructions). Additionally, we’ll select the columns “iucn_2cat”, “Order”, and “Family” which we will use for plotting. Then we’ll remove any rows with an NA value using tidyr::drop_na.
Default bar chart
When creating a bar chart with ggplot2::geom_bar() a categorical variable/column can be mapped to the x aesthetic. The function will then calculate the count numbers.
Create a bar chart of the iucn_2cat variable/column. This is a column of categorical factors (<fct>) representing IUCN categories of:
- LC: Least Concern
- nonLC: non Least Concern including Near Threatened, Vulnerable, and Endangered
amphibian_div_tbl |>
ggplot2::ggplot(aes(x = iucn_2cat)) +
ggplot2::geom_bar()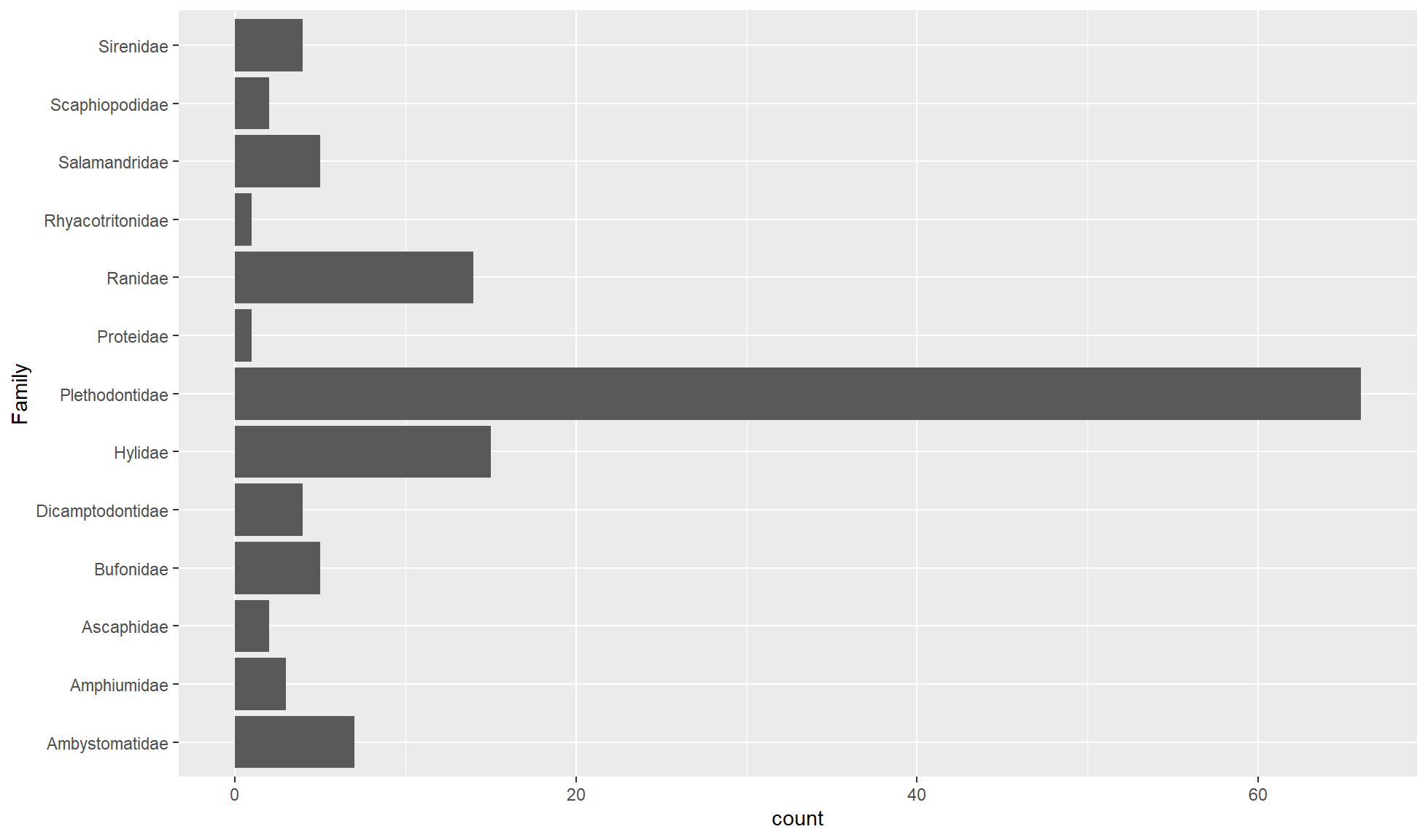
Flipped bar chart
If there are a lot of unique values in the categorical variable you can map it to the y aesthetic to create a flipped bar chart. This is especially useful if the values have long names that would struggle to fit as labels side by side on the x-axis.
Create a flipped bar chart of the Family categorical character variable/column.
amphibian_div_tbl |>
ggplot2::ggplot(aes(y = Family)) +
ggplot2::geom_bar()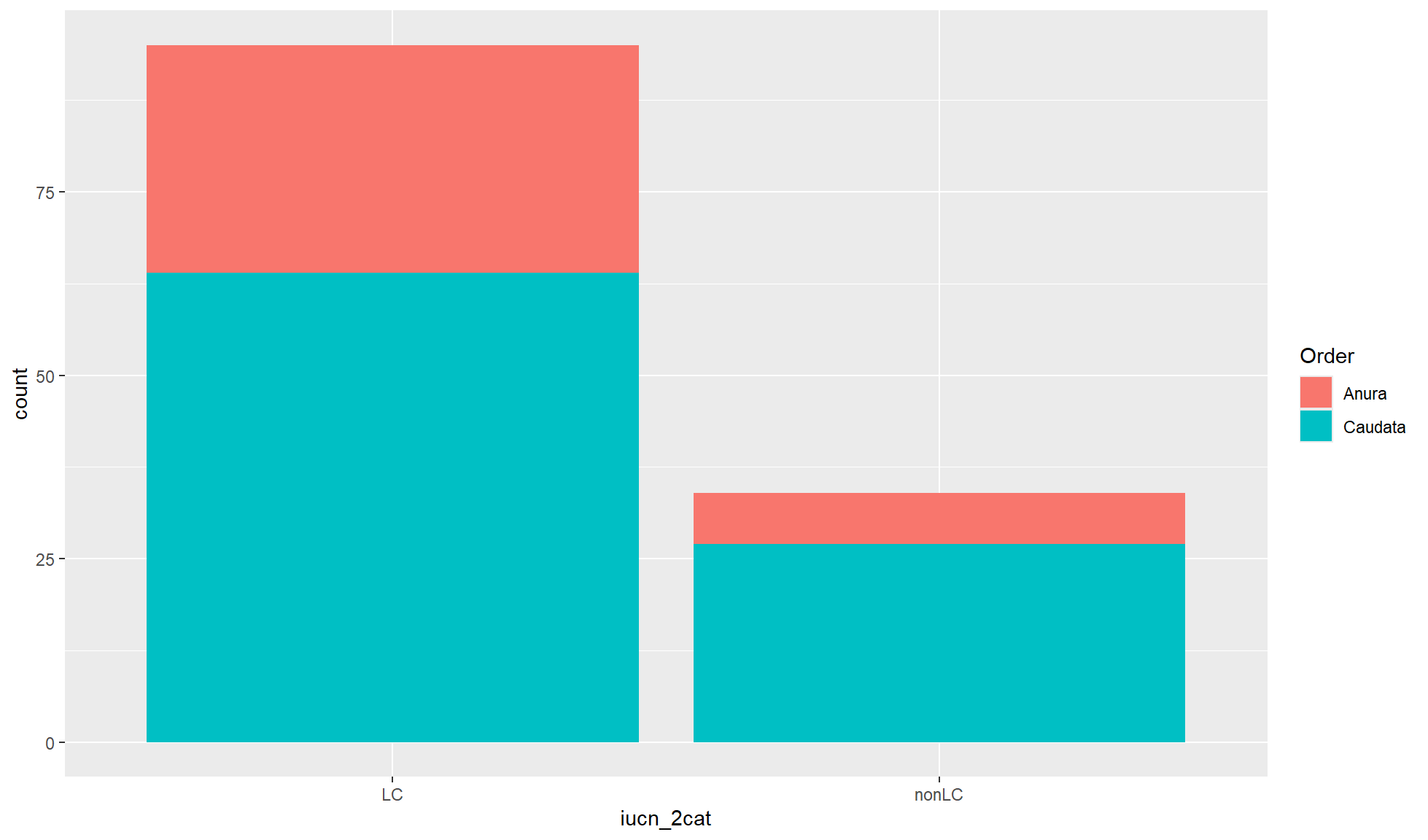
Stacked bar chart
It is common to map a second categorical variable/column to the fill aesthetic. By default this will create a stacked bar chart where the fill variable is represented by colours filling the bar chart. This is useful is you are more interested in the differences between the x-axis groupings.
Create a stacked bar chart of “iucn_2cat” counts where the fill of the bar chart is coloured by “Order”.
amphibian_div_tbl |>
ggplot2::ggplot(aes(x = iucn_2cat, fill = Order)) +
ggplot2::geom_bar()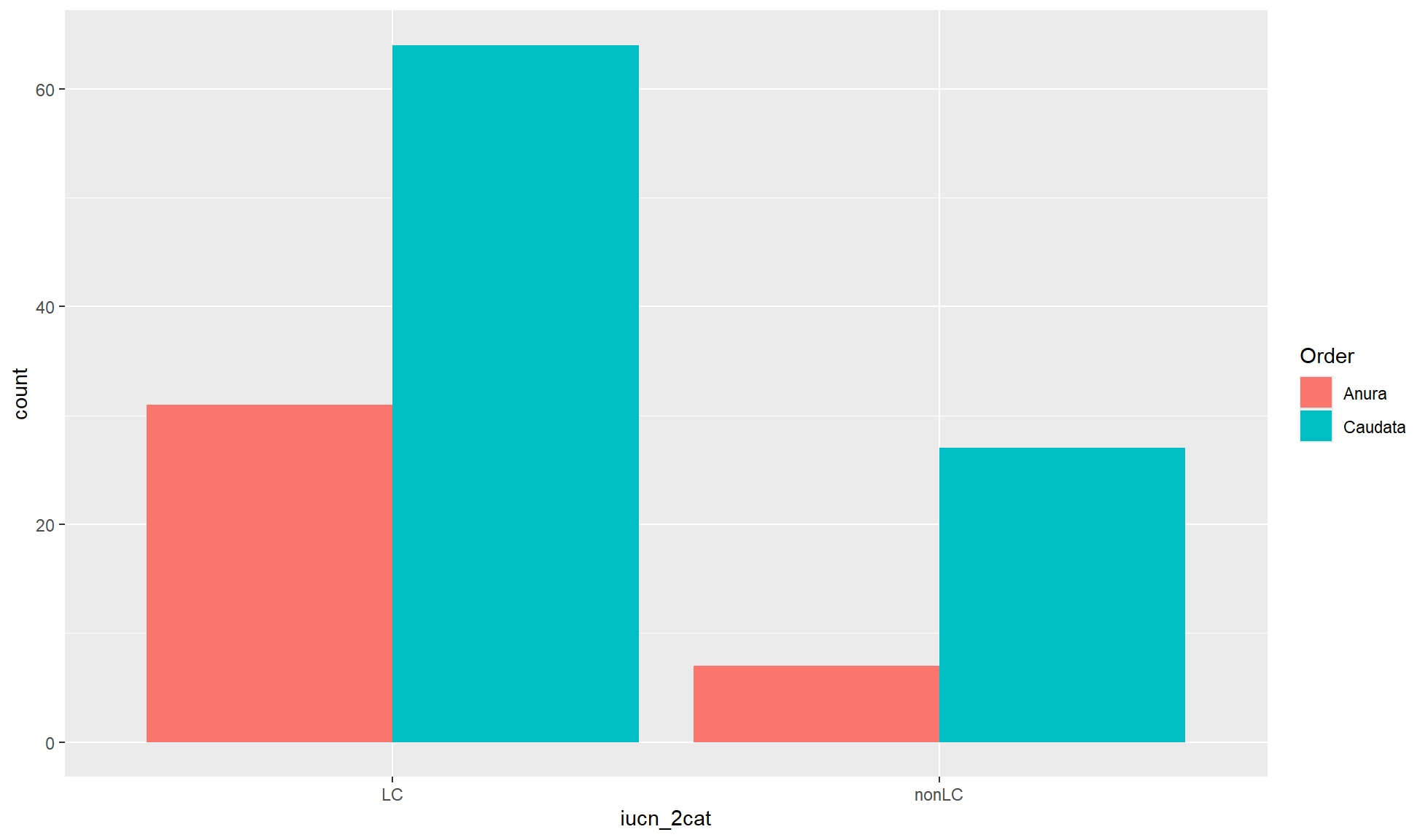
Side-by-side bar chart
When you are interested in the differences within the x-axis groupings you can created a side-by-side bar chart. This is carried out by using the position= option in ggplot2::geom_bar() and setting it to "dodge".
Create a side-by-side bar chart of “iucn_2cat” counts where the fill of the bar chart is coloured by “Order”.
amphibian_div_tbl |>
ggplot2::ggplot(aes(x = iucn_2cat, fill = Order)) +
ggplot2::geom_bar(position = "dodge")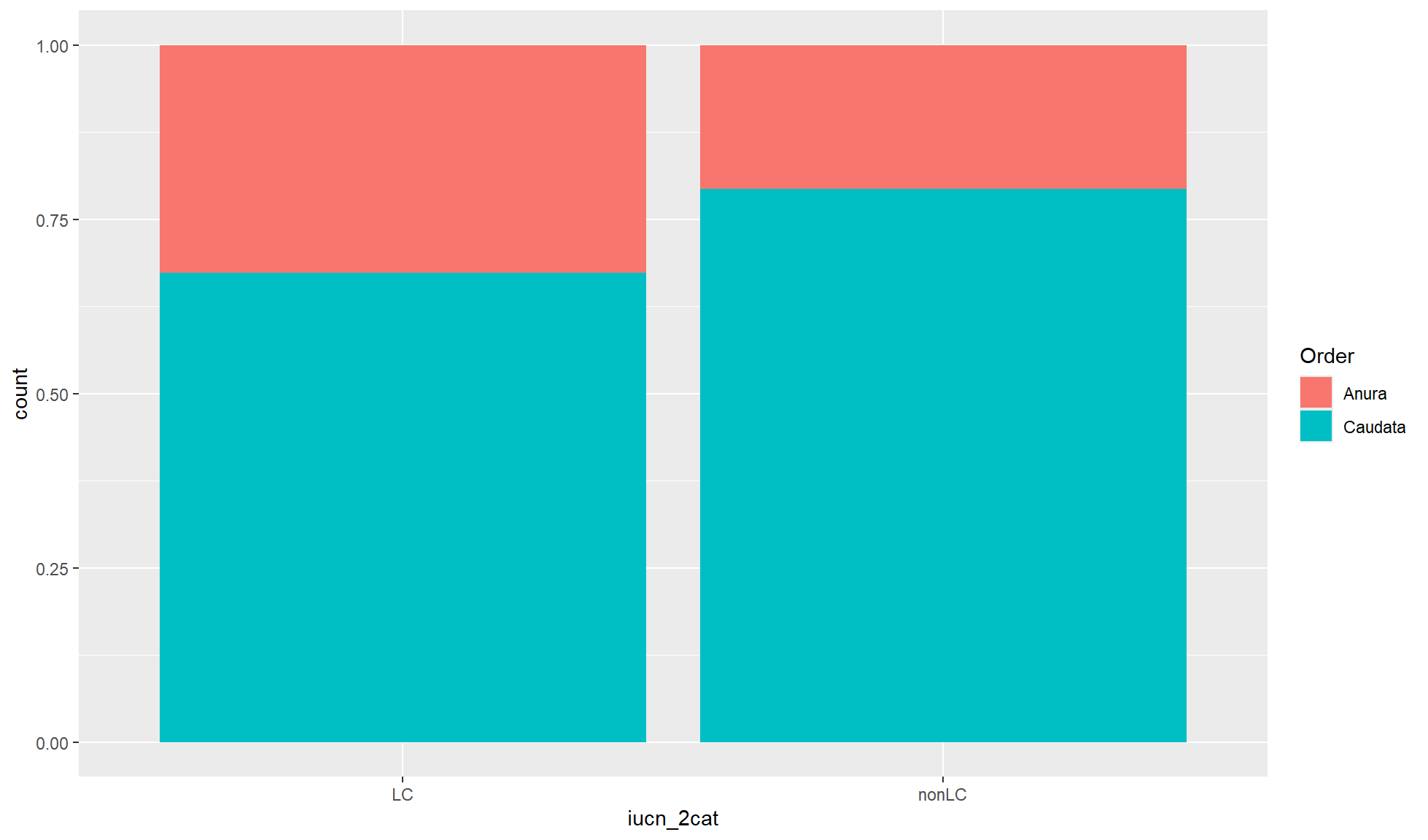
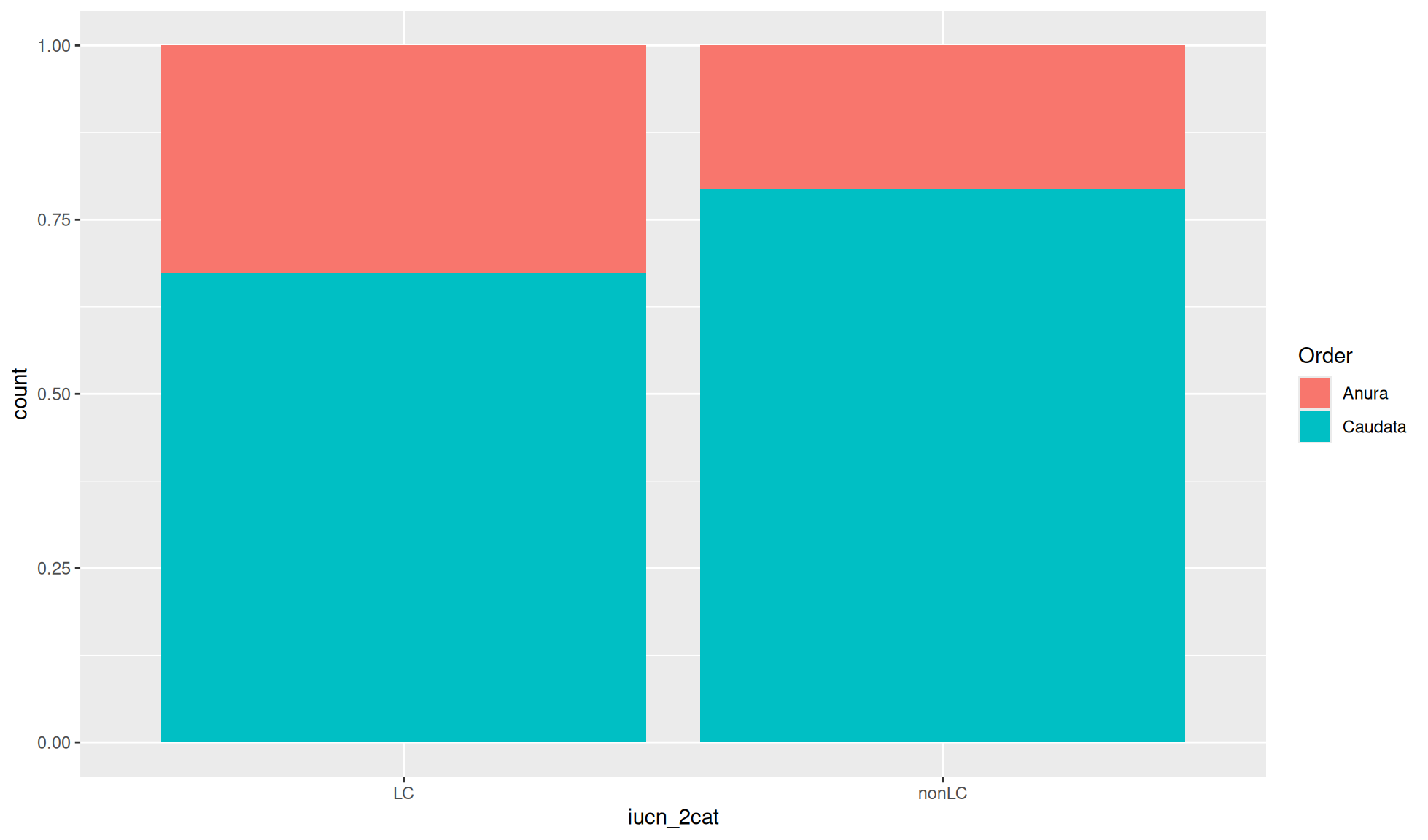
Relative proportion bar chart
ALthough absolute count values are useful for bar charts you will sometimes want relative proportions. To convert the values so the total x-axis count per group equals 1 you can set position= to "fill".
Create a relative proportion bar chart of “iucn_2cat” counts where the fill of the bar chart is coloured by “Order”.
amphibian_div_tbl |>
ggplot2::ggplot(aes(x = iucn_2cat, fill = Order)) +
ggplot2::geom_bar(position = "fill")