Dplyr

Overview
Dplyr is the main data manipulation package for tibbles in tidyverse.
Dplyr is described as a “grammar of data manipulation” using verbs as the name of its various functions.
This website aims to quickly cover the most commonly used dplyr functions and uses. There are a lot more dplyr functions than those covered here. Please check the below link for the full list.
Sections
There are many sections for dplyr. These are summarised below.
Pipes
Pipes (|>) are a vital part of creating efficient and clear code with tidyverse. Pipes allow you to chain/pipe functions together. It can be used for all functions not just those from tidyverse.
Rows
The four main verbs (i.e. functions) to manipulate rows are:
arrange(): Arrange the rows of a tibble. Can be used to reorder the rows based on the values of a column.distinct(): Extracts unique/distinct rows from a tibble.filter(): Extract rows by filtering with conditions. This can be used to pick rows of certain groups, filter based on numeric sizes, and more.slice(): A set of methods to choose a slice of rows based on index positions, top and bottom observations, and min and max values based on a specific column. This is especially useful for piping (|>).
Columns
The six main verbs (i.e. functions) to manipulate columns are:
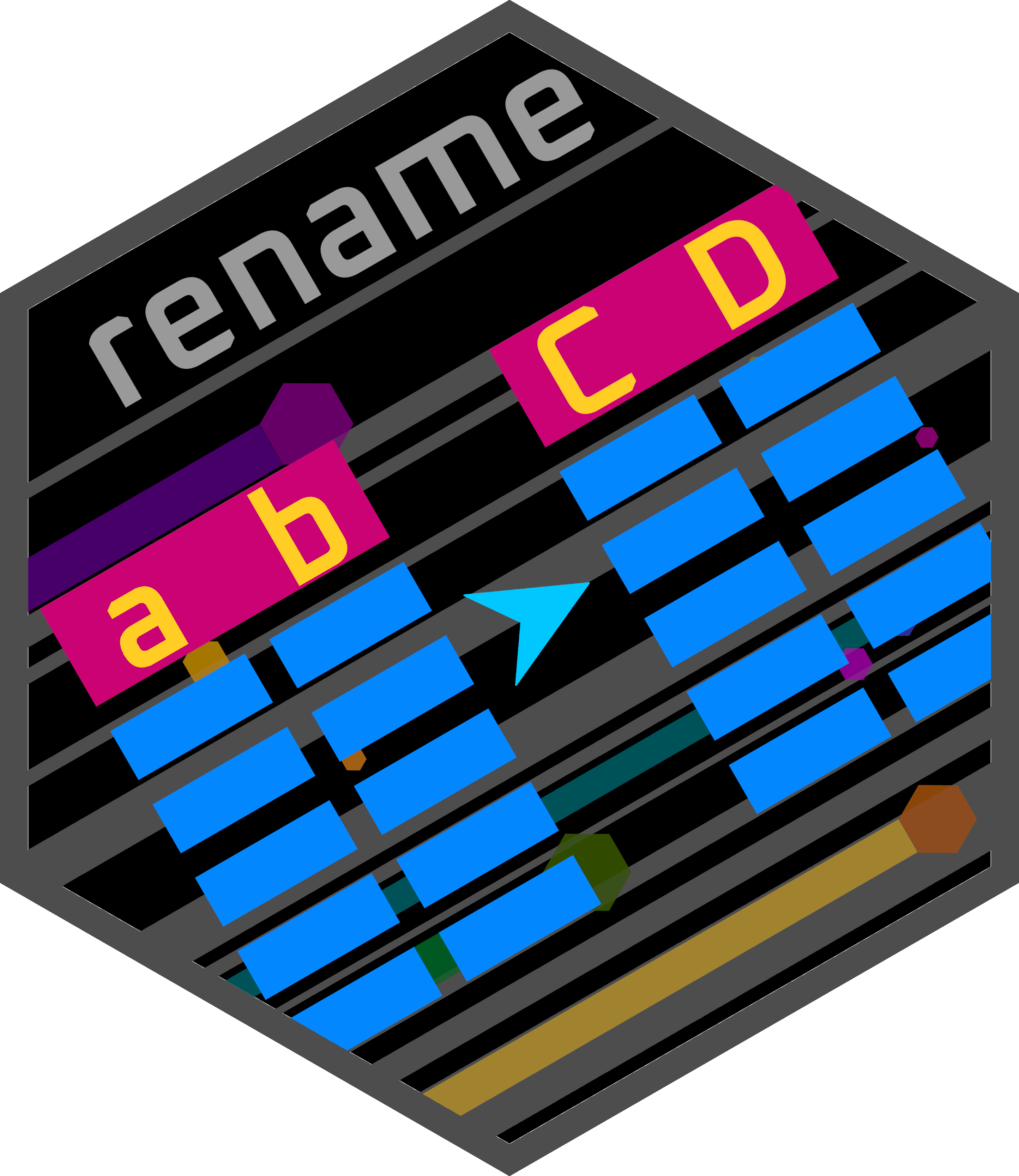
glimpse(): Print a tibble in a transposed manner. Useful for seeing the data types of all the columns.mutate(): Mutate columns to create new columns based on existing ones, modify existing columns, and delete columns.pull(): Pull out a single column from a tibble, resulting in a vector.relocate(): Relocate columns. You can relocate columns to the start or end, and you can move them after or before specified columns.rename(): Rename columns in a tibble.select(): Select specific columns of a tibble. Can be used with a variety of helper functions such asstarts_with(),ends_with(),contains(), andmatches().
If you would like to carry out one of the column functions with multiple columns you can look at the official documentation for the following functions:
Grouping
Tibbles can be grouped by a specific variable/column or multiple variables/columns. This allows for group wise calculations.
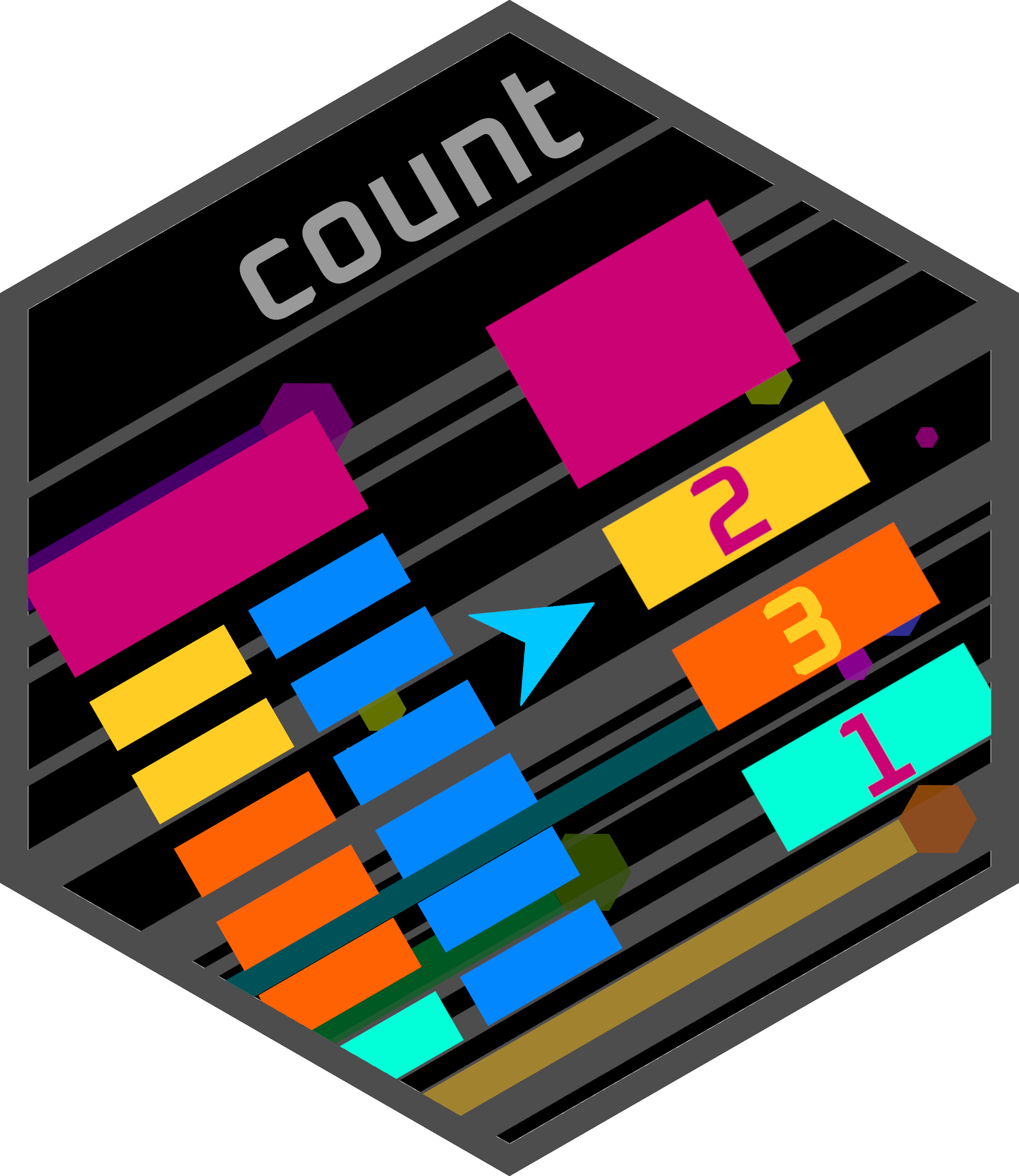
group_by(): Converts a tibble to a grouped tibble.count(): Counts the number of instances of each unique value for the grouping in a tibble.summarise(): Produces a tibble with summary information on the group members in a grouped tibble.- Various functions can be used to calculate summary information including
n(),mean(),median(),sd(),IQR(),first(),last(), andnth().
- Various functions can be used to calculate summary information including
Bind tibbles
Tibbles can be combined/bound together with the following functions:
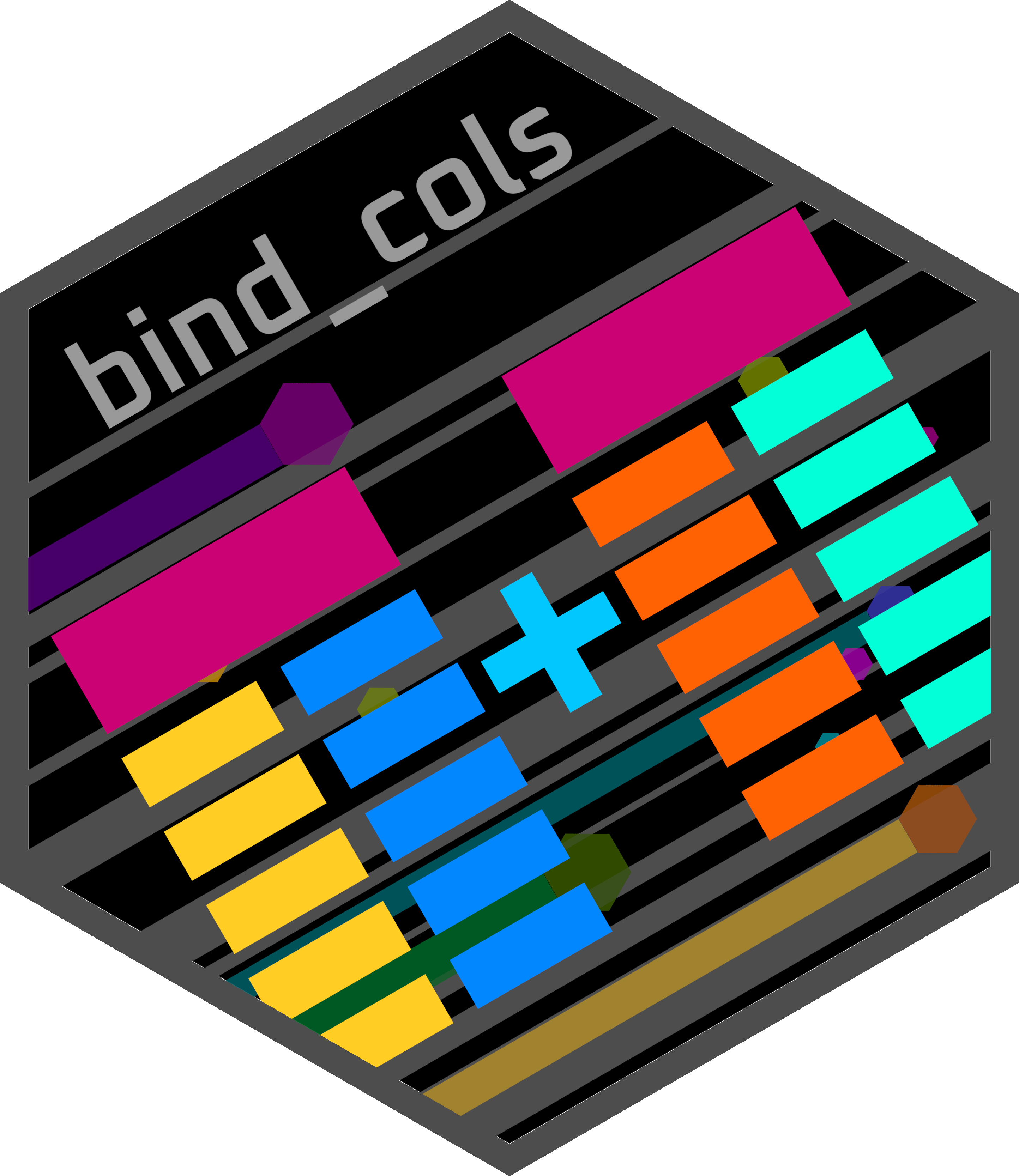
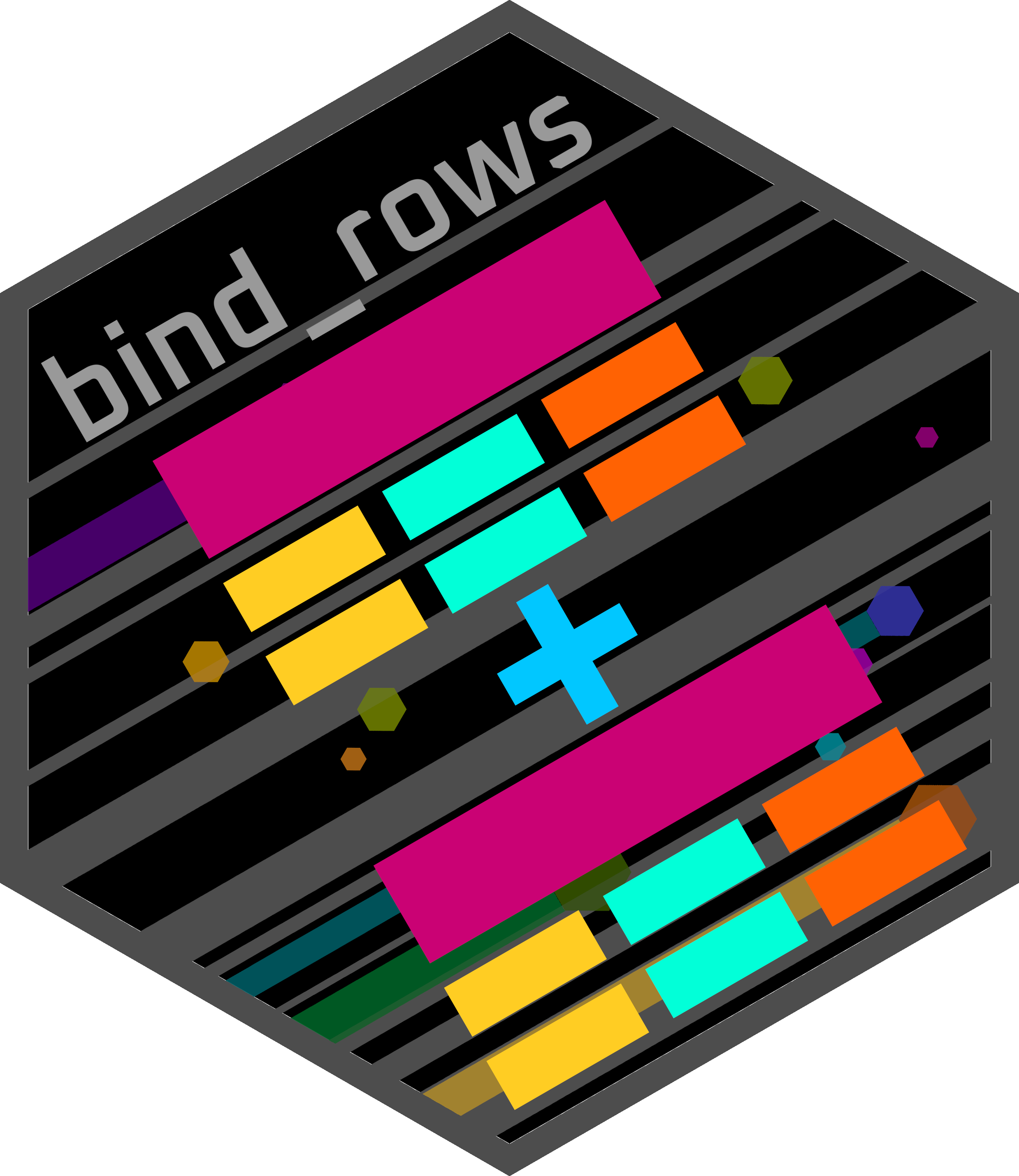
bind_cols(): Bind 2 tibbles by columns (i.e. bind the tibbles side by side). The two tibbles must have the same number of rows.bind_row(): Bind 2 tibbles by rows (i.e. bind one tibble on top of the other ). The two tibbles must have the same column types and names.